Overview
Genital Warts
Cervical Dysplasia and Cervical Cancer
Symptoms
Causes
Prescription
Health Tips
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) refers to a group of viruses that are extremely common and contagious. There are over 150 different strains, some of which are responsible for the common wart, while more than 40 are passed through sexual contact. HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection worldwide. Most people who are sexually active will contract at least one of the many HPV strains at some point in their lives.
In most instances, the immune system will fight off the virus and no symptoms occur. There are both low- and high-risk strains of HPV. Low-risk strains, such as types 6 and 11 are more common but rarely cause cancer, however they cause around 90 percent of all genital warts. Type 11 may also bring about slight changes to the cells of the cervix. High-risk types are those that lead to cervical dysplasia, and cancers of the cervix, anus, throat, mouth, or penis. While there are about a dozen high-risk strains, types 16 and 18 are the most concerning as they cause around 70 percent of cervical cancers.
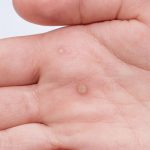
Genital Warts
Venereal warts (condylomata acuminata) may be found on the genitalia, anus, and the mouths of both men and women. When warts appear on the cervix, it is critical they be treated aggressively. Genital warts are a sign of a weakened immune system.
Cervical Dysplasia and Cervical Cancer
Cervical dysplasia is the term for abnormal growth or changes to the cells on the surface of the cervix. It is more common for women in their 20’s and 30’s but may occur at any age. Mild or low-grade changes will often clear on their own, however changes must be monitored closely to ensure they do not become more severe and lead to cancer. The American College of Pathology states that 4 out of 5 women who die of cervical cancer have not had a pap smear in the previous five years.
If cervical dysplasia can be caught early enough during a pap, cervical cancer can be prevented. Regular pap tests are extremely important, and not just for young women.
According to Health Canada, the highest incidence of cervical cancer and the highest death rates occur in women over the age of 65, a group that often stops having annual pap tests. Canada’s guideline for pap tests vary slightly by province, but in general, it is recommended that sexually active women begin testing at age 21 and repeat every three years until they reach 69. However, a 2017 study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that cervical cancer rates rose until age 70, and did not decline until after age 85 in women who have not had a hysterectomy. Every adult woman from the age of 18 on should have a pap test annually to ensure her cervix is healthy.
Symptoms
With the exception of HPV strains that cause genital warts, there are no symptoms until an abnormal pap smear or invasive cervical cancer is apparent. This is why an annual pap test is necessary. Although less common, HPV may lead to vulvar, vaginal, penile, anal, mouth, and throat cancers.
Genital warts are red or pink, flat or tall, and can surface in groups or individually. Standard medical treatments to remove genital warts are less than satisfactory, and most often the warts frequently return.
Causes
HPV infection is caused by coming into contact with the virus, typically through sexual intercourse or skin-to-skin contact. Non-sexual transition of high-risk HPV strains is rare but can occur. While one can reduce risk by limiting the number of sex partners and using condoms, most people will still come into contact with the virus. Having a sexual partner who has had multiple partners, and becoming sexually active before the age of 18, will increase chances of exposure.
The main risk factors that hinder the body’s ability to fight off HPV viruses include:
- Immunosuppressing drugs
- Increasing age
- Nutritional deficiencies of folic acid, vitamin A and vitamin C
- Smoking
- Use of oral contraceptives
Birth Control Pill
Long term use of the pill can increase the risk of cervical cancer, with the risk being even greater for those who have HPV. The birth control pill depletes the body of vitamins B6, B12, and C, folic acid, zinc, and riboflavin. Cervical dysplasia and low levels of the B vitamins have been linked. If possible, opt for another form of contraceptive such as the copper IUD. Research shows that the use of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD) may reduce the chance of cervical cancer by a third.
Abnormal PAP Tests
Do not ignore abnormal pap tests. In North America, pap results are graded as CINI, CINII, CINIII, or CINIV or CIS. A CINIV or CIS grade indicates cancer. Most women are not treated until they have an invasive CINII or CINIII result. The Bethesda system of grading pap tests is also used, and tests are graded as Low-Grade SIL (LSIL, equivalent to a CINI) and High-Grade SIL (includes HSIL, CINII, CINIII and Cancer).
Too many women are advised they have an abnormal test result and told to come back in six months for another test, but are not given any suggestions for how to get their cervical cells to return to normal. Some abnormal cells return to normal with no treatment; simply taking a nutritional supplement containing indole-3-carbinol (I3C), calcium d-glucarate, and sulforaphane along with vitamin A, C and folate could help ensure a normal pap test. Every woman should take a multivitamin with minerals to help those abnormal cells revert back to healthy cells.
New research has shown that indole-3-carbinol (I3C) can reverse abnormal cervical lesions before they have a chance to develop into cancer. In one study, 30 women with CINII and CINIII cervical lesions took 200 mg of I3C daily. Fifty percent in the treatment group had complete regression of their lesions. None of the placebo group had complete regression of their lesions.
Gardasil Vaccine: An HPV Experiment
HPV 16 and HPV 18 are thought to be responsible for about 70 percent of cervical cancers. The Gardasil vaccine is believed to protect against these strains, as well as HPV 6 and 11. HPV 6 and 11 cause 90 percent of genital warts but do not increase cancer risk. GlaxoSmithKline has also launched the Cervarix vaccine for HPV 16 and 18.
Gardasil is currently being recommended for girls and women aged 9 to 26, although few girls participated in the studies. Eleven thousand women— but no minors—took part in the vaccine trials. In the Canadian Medical Association Journal, researchers cautioned that while the vaccine appears to effectively prevent HPV 16 and 18 infection, reducing such infections does not necessarily translate into fewer cervical cancer deaths. They also noted that there are many gaps in knowledge about this vaccine. Vaccine recommendations now include boys and men ages 11 to 21, and for gay and bisexual men through to age 26.
An editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association noted that, between June 2006 and December 2008, 23 million doses were administered, causing 12,424 adverse events. Minor events included local site reactions, headaches, hypersensitivity reactions and hives. Overall, 772 events (6.2 percent of the total number of adverse events) were serious and included 32 deaths. Serious events included complications such as blood clots, Bell’s palsy, seizures, paralysis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Prescription for Health
Diet
Avoid margarine and low-quality or rancid fats such as canola, soy, cottonseed, or safflower oil. Include virgin coconut oil, extra-virgin olive oil, and organic grass-fed butter.
Avoid or greatly reduce sugar, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods. Instead opt for whole grains such as millet, amaranth, oats, quinoa, and brown rice. Include legumes, seeds, nuts and quality proteins, such as wild salmon or mackerel, and organic chicken or eggs.
Eat foods that help to support the immune system. Include lots of vegetables and fruit. Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage are especially important.
Fresh garlic, ginger, and turmeric should be included in the diet.
Lifestyle
Condoms are very effective at preventing the transmission of HPV. Reduce exposure to the virus by not having unprotected sex. Contracting the virus is more likely by having unprotected sex with people who have genital warts or who have come into contact with genital warts. Do not assume that a person is not infected because there are no visible warts.
Have pap smears every year to detect early changes in the cervix. If one suspects genital warts, seek attention from a medical or naturopathic doctor. While natural therapies can be effective at reversing cervical dysplasia, the condition should be supervised and evaluated for changes in the cervix.
Quit smoking as soon as possible. The incidence rate of cervical dysplasia is two to three times higher in smokers. Smoking reduces the body’s ability to fight off HPV and increases the chances of developing cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer.
Supplements
Take plant sterols and sterolins. Over 65,000 cases of cervical cancer are diagnosed each year in North America, and over 10,000 women will die as a result. The fear of cervical cancer sends most women to their doctor for an annual pap smear. Often women are told that their pap smear is abnormal, showing cell changes associated with cervical dysplasia. As mentioned earlier, many have HPV-induced cervical dysplasia. A small pilot study using Moducare brand plant sterols and sterolins was undertaken to see if HPV-induced cervical dysplasia could be reduced or reversed by enhancing immune function.
Thirteen women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, low-grade squamous epithelial lesion (CIN III) showing cervical lesions were divided into two groups. Seven were given Moducare and six were given a placebo. The results of the study showed that all six in the placebo group had no improvement of disease. In the treatment group receiving Moducare, the lesions were completely eliminated in three patients, while the other four showed no further progression of the lesions. Although this was a small sample, it provides enough encouragement that further research should be performed.
| Nutrient | Dosage | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Moducare® (Beta-Sitosterol, Beta-Sitosterolin-Beta-D-Glucoside) | 20 mg / 0.2 mg Adults and children 17 years and older take 1 capsules three times daily OR 2 capsules upon rising and 1 capsule before bed. | Helps support a healthy immune balance; reverses HPV cervical abnormalities |
| Calcium D-glucarate* | 300 mg | Important for healthy metabolism of estrogen; supports normal cell growth |
| Curcumin* (95% curcumin) | 100 mg
| Prevents abnormal cell growth, detoxifies cancer causing forms of estrogen, enhances progesterone |
| Indole-3-carbinol* | 300 mg | Stops healthy estrogen from converting into the cancer-causing forms
Has been shown to reverse abnormal PAP tests within three menstrual cycles. Inhibits HPV from causing cancer |
| Green tea extract* | 200 mg | Protects against abnormal cell growth; detoxifies excess estrogens; improves treatment response time |
| Rosemary extract* | 50 mg | Reduces tumor formation; is antioxidant |
| Di-indolylmethane (DIM)* | 100 mg | Antioxidant; reduces risk of cancer |
| Sulforaphane * | 400 mcg | Reduces risk of cancer; stops abnormal cell growth |
| Borage Oil
| 2000 mg daily | Anti-inflammatory; controls negative prostaglandins involved in pain and inflammation |
| Coenzyme fully reacted B-complex: | Look for a minimum of the following per daily dose: B1 100 mg B2 7.5 mg Niacin 353 mg B5 300 mg B6 100 mg B12 1000 mcg Folate 1000 mcg | Those with low levels of B12 and folate are at an increased risk of cervical cancer from HPV |
| Vitamin C | 1000 mg daily | Those with highest vitamin C levels had an 80 percent reduced risk of cervical cancer |
| Beta glucans 1,3/1,6 | 250 mg daily with food | Strengthens immune system, enhances T cells and natural killer (NK) cells |
| Bifidobacterium longum (100% BB536) | 5-10 billion active cells | Within six months of taking probiotics 29 percent of women were clear of HPV |
Health Tips to Enhance Healing
- Choose another form of birth control other than the pill if possible.
- Have pap smears annually to detect early changes in the cervix.
- Never have unprotected sex.
- Stop smoking.
- Stress reduction is important to keep cortisol levels in check. Cortisol is implicated in increasing risk of viral infections.
- Take plant sterols and sterolins.