Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Prescription
Health Tips
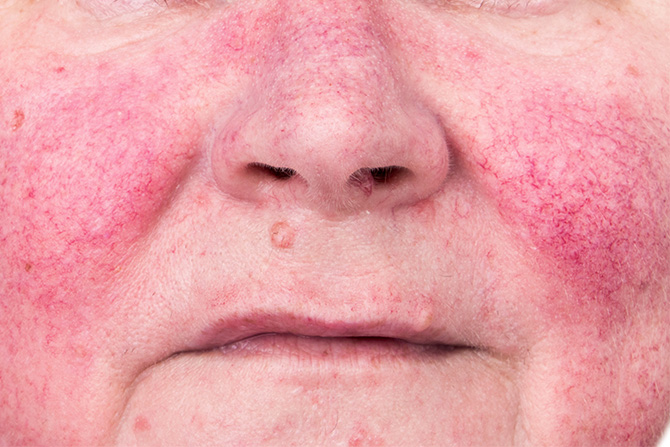
Rosacea is a chronic skin disorder causing acne-like breakouts, broken blood vessels and flushing redness mostly on the cheeks and nose. Rosacea generally strikes people after the age of 30. It affects three times more women than men and is more common in those with fair skin. If the problem is not addressed, rosacea can cause permanent damage to the skin.
Symptoms
It usually begins with a flush of the face that comes and goes, and tiny bumps may appear. A network of blood vessels may be seen beneath the surface of the skin, and as the disease progresses the redness gets worse. If the skin swells, it may be tender. The eyes may become red, sore, or swollen, even to the point where vision is affected. The skin may thicken over time causing a red bulbous nose called rhinophyma, which is common in men but rare in women.
Causes
Although the cause of rosacea is not known, there are a number of triggers specific to each individual that aggravate the condition, and may include:
- Caffeine
- Excessive use of alcohol
- Exercise
- Exposure to sunlight
- Food and environmental allergies
- Gingko biloba
- Hot liquids
- Infection
- Lack of stomach acid or the digestive enzyme lipase
- Menopausal flushing
- Smoking
- Spicy foods
- Stress
Nutritional deficiencies of vitamins A and B2 are also linked to the development of this condition. Rosacea is often related to excess sebum production. Rhinophyma is common in alcoholics and those who drink alcoholic beverages daily. Research studies have found that those with rosacea often have a riboflavin deficiency and/or low stomach acid.
Prescription for Health
Diet
Certain foods may trigger rosacea, but the problem foods vary from person to person. Keeping a food diary may help to pinpoint foods that should be avoided. Examples of potentially problematic foods are histamine releasing foods such as citrus fruits, strawberries, food preservatives and flavourings, as well as high histamine containing foods such as tomatoes, eggplants, vinegar and cured meats.
Eat foods that encourage healthy liver function, such as artichokes, rhubarb, Chinese white radish, black radish, soy, apples, and rolled oats.
Lifestyle
People with rosacea almost always have skin that is sensitive to many skin care products. In this case it is recommended to just try one product at a time, and initially apply it only every second day to determine tolerance. Products with low levels of retinol, coffeeberry and green tea are often tolerable for rosacea patients if introduced slowly to their skin care regimen. Use all natural, mineral-based makeup and choose unscented soaps, cleansers, and shampoos. Avoid perfumes and scented body sprays.
Wash pillowcases regularly. Avoid using detergents or shampoos with perfumes, scents, colors, or fragrances. Rinse all bedding twice.
The chronic redness and broken capillaries seen in rosacea may also be diminished with intense pulsed light (IPL) and/or a pulse dye laser. Several treatments are often required to fade the red spots. In addition to fading the redness, IPL also results in the formation of new collagen in the skin. This improves the ruddiness often associated with rosacea.
| Nutrient | Dosage | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 5000 IU daily | Required for healing skin |
| Coenzyme fully reacted B-complex: | Look for a minimum of the following per daily dose:
B1 – 100mg B2 – 7.5 mg Niacin – 353 mg B5 – 300 mg B6 – 100 mg B12 – 1000 mcg Folate – 1000 mcg |
Reduces stress; deficiency has been seen in those with rosacea |
| Vitamin C | 500–1000 mg twice daily | Enhances collagen formation |
| Vitamin E | 200–400 IU daily | Important for skin repair |
| Bifidobacterium
BB536 |
2.5 billion active organisms daily | Improves digestion by increasing intestinal flora |
| Borage oil | 2000 mg daily | Is beneficial to the skin and anti-inflammatory |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | 750 mg EPA
500 mg DHA |
Helps to reduce skin inflammation |
| Zinc | 30 mg daily | Prevents rosacea |
| Digestive enzyme | 500 mg before meals | Improves digestion and metabolism of fats |
| Celadrin topical cream | Topically applied throughout the day | Anti-inflammatory reduces redness and calms capillaries, heals skin barrier |
Health Tips to Enhance Healing
- Eliminate sugar, dairy, and hydrogenated fats. This is essential to halting rosacea.
- Alcohol is a very strong trigger for rosacea, so reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Allergies are also implicated in rosacea. Ask for a referral to an allergy specialist and get tested for possible food and environmental triggers.
- Antibiotics have been effectively used to treat rosacea in some cases. If using antibiotics, take probiotic supplements as well.
- Avoid extreme heat or cold, such as saunas, hot tubs, hot baths, outdoor winter activities.
- Do not consume hot food and drinks. Let them cool to room temperature first.
- Drink plenty of pure, filtered water daily. Water flushes out toxins and encourages efficient elimination.
- Eat foods that encourage healthy liver function.
- If low stomach acid is suspected, it may also be hindering digestion.
- Protect face during extreme heat with big hats or umbrellas, and in cold temperatures with hats and scarves.
- Reduce stress as it may aggravate rosacea.
- Take two capsules of digestive enzymes before every meal.
- Use all-natural, mineral-based makeup and unscented skin care; avoid using conventional cosmetics or heavy moisturizers.
- Use Hauschka Rythmic Skin Conditioner (Sensitive) every night for three months to reduce the appearance of rosacea.
- Wash face with natural soaps or cleansers and keep hair clean.