Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Prescription
Health Tips
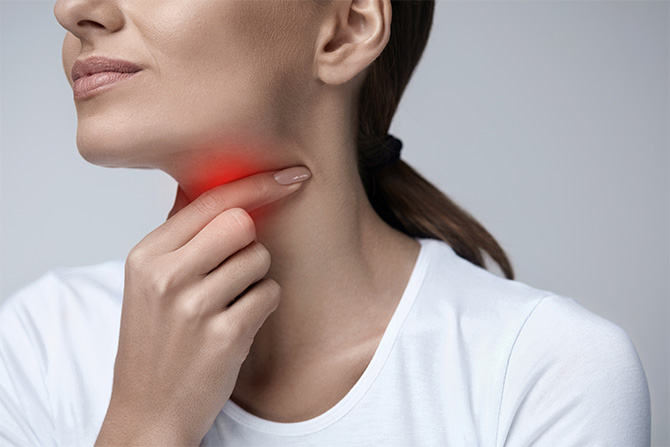
A sore throat is an extremely common health annoyance that most people have suffered at one time or another. As part of the body’s frontline of defence, the throat is a barrier that comes in contact with germs and environmental irritants. A sore throat, often accompanied by a cold, is usually the first sign or symptom of an infection and may last only a few days.
Symptoms
Symptoms and intensity can vary depending on the severity of a sore throat.
- Hoarse voice, especially if larynx becomes inflamed or infected
- Mild to excruciating pain
- Raw, itchy, burning, stabbing, or tender feelings in the throat
- Red, swollen tonsils with white patches
- Swallowing or coughing may become extremely painful
- Swollen and tender lymph glands located under the jaw at each side of the neck
Causes
As with fever, a sore throat is an indication that a bacterial or viral infection such as tonsillitis, sinusitis, or mononucleosis is present. Removal of the tonsils is not recommended as they are an integral part of the immune system and a significant component of the body’s defences. Antibiotics will not help a sore throat if the cause is viral, and several studies have shown that even when throat infections are bacterial, they are generally self-limiting, and in some studies patients using antibiotics fared no better than no treatment at all.
Streptococcus bacteria, which cause strep throat, can only be diagnosed by a throat culture. Fortunately, rapid result cultures are available that can determine if the infection is in need of antibiotic therapy. Physicians are trained to prescribe antibiotics in the presence of strep infection, even though research has shown that recovery rates were the same whether people were given the antibiotic or allowed the bacteria to run its course. Antibiotics are essential in the case of those who are immune-compromised, or who have kidney disease or a history of rheumatic fever. In rare cases step throat can cause serious complications, especially in the young, old, or those with weakened immune systems.
Exposure to excessive amounts of dust, smoke, dry air, a postnasal drip, or acid reflux may irritate the throat. Sometimes the throat suffers abrasions from swallowing very hot foods or drinks, or when one has been talking, yelling, singing, or coughing loudly for long periods of time. Other causes of a sore throat include allergic reactions and tooth or gum infections. In rare cases, a tumour, or STI (gonorrhea, chlamydia) in the throat may cause soreness.
The throat is fairly resilient against invaders, so when it succumbs to infection, it means that the immune system was too weak and unable to adequately mount a counterattack to destroy the virus or bacteria. If one suffers chronic throat infections, it is important to support the immune system.
Prescription for Health
| Nutrient | Dosage | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Moducare®
(Beta-Sitosterol, Beta-Sitosterolin-Beta-D-Glucoside) |
20 mg / 0.2 mg
Adults and children 17 years and older take 1 capsules three times daily OR 2 capsules upon rising and 1 capsule before bed. Children 5 to 10 years take 1 capsule or chewable tablet, one to two times daily. |
Helps to support a healthy immune system balance |
| Vitamin A (micellized, liquid) | 6000 mcg RAE in the back of the throat daily for five days. Allow it to bathe mucous membranes. 1500 mcg RAE thereafter. | Fights bacterial and viral infections, and often alleviates pain of sore throat immediately |
| Vitamin C with bioflavonoids | 1000 mg of vitamin C three times daily; 500 mg of bioflavonoids three times daily. | Boosts immune function; is antiviral, antibacterial, antihistamine; speeds up healing of mucous membranes |
| Zinc lozenges | 30 mg per day during infection. | Alleviates pain and supports immune system. Do not be tempted to eat all of the throat lozenges in one day. Too much zinc can suppress immune function. |
| Garlic (Kyolic) | Two or three capsules three times daily | Acts as an antiviral and antibacterial |
| S. Salivarius (K12) | 5 billion (cfu)
Suck 5 lozenges per day during infection |
Increases antiviral interferon reduces inflammatory 12-8. Treats strep and tonsillitis sore throat |
| Goldenseal, standardized to berberine | Suck 5 lozenges per day during infection | Enhances immune function, is antibacterial. Look for goldenseal throat spray at your health food store. |
Health Tips to Enhance Healing
- Apply warm throat wraps of big cabbage leaves on an hourly basis. It is amazing how effective this can be.
- Drink plenty of herbal tea and unsweetened cranberry juice mixed with water.
- Gargle every few hours with water, apple cider vinegar, and 1 tsp (5 mL) of sea salt. Gargle solutions can also be made with herbs such as sage, licorice, and fenugreek.
- Get tested for food allergies and environmental allergies, if a cough or tickle is constant or recurring.
- If pain is causing loss of sleep or making it difficult to eat, a pain killer such as ibuprofen or paracetamol may help reduce the pain to a bearable level.
- Stop smoking. Tobacco leaves a film of tar on the tongue, teeth, and gums that can make infections worse and delay healing. It may also lead to oral cancer.
- Sugar suppresses the immune system, and should be eliminated as much as possible from the diet. Do not drink concentrated fruit juice as these are also high in sugar. Keep honey and maple syrup to a minimum.
- Throat lozenges containing echinacea, vitamin C, goldenseal, and cherry bark are soothing to inflamed throat tissues. Use as directed.
- Use garlic frequently and liberally in meals.
- Water is the cheapest virus fighter. Drink 8 to 10 glasses during infection to help wash away infection.
- When brushing teeth, also brush the tongue or use a tongue scraper to remove bacteria that are hiding on the surface. Change toothbrush once illness has passed, and thereafter change it monthly to avoid the growth of bacteria.
- When taking antibiotics, eat plain yogurt or supplement with probiotics to restore the “friendly” bacteria that will be destroyed.