Overview
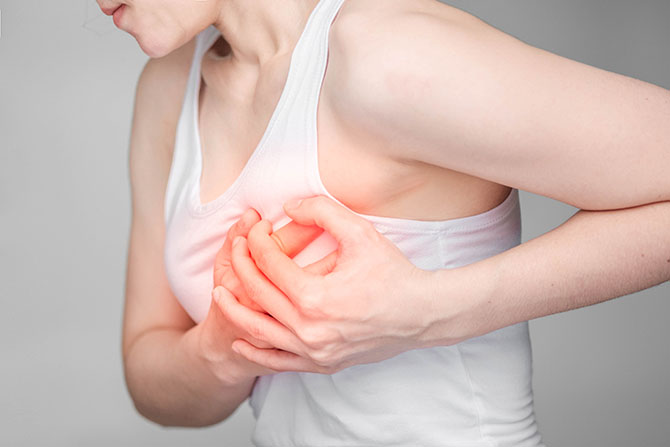
Symptoms
Causes
Prescription
Health Tips
Fibrocystic breasts, also called cystic mastitis, is a common, non-cancerous condition that is no longer considered a disease. Breasts are a mixture of fat, glands and connective tissue so their texture is always irregular. Over 60 percent of women experience fibrocystic breasts at some point in their lives.
Most women affected are between the ages of 30 and 50, with symptoms generally disappearing after menopause. It may go unnoticed, be mildly uncomfortable, or severely painful, especially when breasts become swollen. Fluid that has not been drained via the lymphatic system fills in small spaces within the breast. The fluid is then encapsulated by fibrous tissue and thickens like scar tissue. The cysts may swell before and during menstruation.
With the fear of breast cancer so prominent today, breast lumps are a concern for many women. Although fibrocystic breasts can make detecting cancerous tumours difficult during a breast self-exam, they do not increase one’s risk of cancer.
Symptoms
Symptoms are typically worse before menstruation and change throughout the month:
- A lumpy feeling or thickening to the breast
- Breast pain during ovulation
- Breast tenderness and swelling
- Changes in breast lumps during menstrual cycles
- Changes to the breast tissues in both breasts
Causes
Breast tissues are affected by a woman’s monthly hormonal cycle. During the cycle, milk-secreting glands enlarge with fluid and their cells multiply. Most of the excess fluid is reabsorbed or drained by the lymphatic system. This process occurs every month during childbearing years. In some women this process causes fibrous tissue to develop into lumps.
An excess of prolactin or estrogen may cause fibrocystic breast changes to occur. An imbalance in the ratio of estrogen to progesterone in the body due to stress, estrogen replacement therapy or xenoestrogens exposure may also be contributing causes. Young women with irregular periods are at an increased risk due to fluctuating hormone levels. Heavy coffee consumption, a diet high in bad fats, and high alcohol intake are all risk factors. Lumps often disappear after menstruation when hormone levels return to normal. Because of this, it is considered a symptom of PMS.
Prescription for Health
Finding lumps and irregularities in the breast can be stressful. Monthly breast self-exams, infrared breast scans and/or ultrasound can help reduce fears of breast cancer. Although most lumps are benign, if one is discovered, get a physician’s assessment. If one finds lumps that suddenly grow larger but do not change during the menstrual cycle, nipple discharge, severe breast pain that does not go away, or puckered or dimpled skin on the breast, then a physician should be consulted immediately.
| Nutrient | Dosage | Action |
|---|---|---|
| D-glucarate* | 150 mg | Important for healthy metabolism of estrogen; supports normal cell growth |
| Curcumin (95% curcumin) | 50 mg | Prevents abnormal cell growth, detoxifies cancer-causing forms of estrogen |
| Indole-3-carbinol (I3C) | 150 mg | Stops healthy estrogen from converting into cancer-causing forms
Has been shown to reverse abnormal PAP tests within three menstrual cycles |
| Di-indolylmethane (DIM) | 50 mg | Antioxidant; reduces risk of cancer |
| Sulforaphane | 200 mcg | Reduces risk of cancer; stops abnormal cell growth |
| Topical Iodine | Start one week before menstruation for best results.
Five percent solution for seven days, then stop for seven days, repeat for seven days. |
Important for thyroid activity
Deficiency of iodine promotes FBD symptoms |
| Chaste Tree Berry (Vitex)* | 100–175 mg daily | Balances estrogen-to-progesterone ratio; important for proper cell function |
| Natural Progesterone Cream |
In Canada, progesterone cream is a prescription drug
Use 6 percent natural progesterone 1/4–1/2 tsp morning and night between days 5–28 (or whenever your normal cycle ends) In the U.S., my choices are Emerita Pro-Gest single use packets and Progesta-Care by Life-flo; the latter delivers 20 mg in a pre-measured pump dose |
Restores progesterone levels and alleviates estrogen-dominant symptoms |
| Borage Oil
|
2000 mg daily | Anti-inflammatory; controls negative prostaglandins involved in pain and inflammation |
Health Tips to Enhance Healing
- Avoid antiperspirants; they clog up drainage from the sweat glands and the toxins have to drain back into the breast.
- Avoid caffeine, chocolate, tea and cola drinks as they contain methylxanthines that cause fibrocystic breasts.
- Avoid parabens found in body care products as they have an estrogenic affect and have been linked to breast cancer.
- Conduct breast self-exams monthly. It is important to be familiar with breast tissue consistency to detect any subtle changes, such as thickening, lumps, etc., as well as when they may occur or disappear.
- Detoxification and elimination of waste is very important. Eat liver-friendly foods such as lemons, onions, garlic, leeks, kale, carrots, beets, artichokes, and members of the cabbage family (broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower).
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and help to detoxify and manage weight.
- Massaging breasts in a circular motion will improve lymph flow and circulation, and if done daily, will help increase familiarity with breast tissue. Make it a ritual, either during daily shower or before bed.
- Reduce estrogen levels, follow an organic, predominantly vegetarian diet, and increase fibre intake. Fibre carries estrogen out of the body.
- To control pain, use castor oil packs
- Treat constipation to ensure elimination of toxins.