Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Prescription
Health Tips
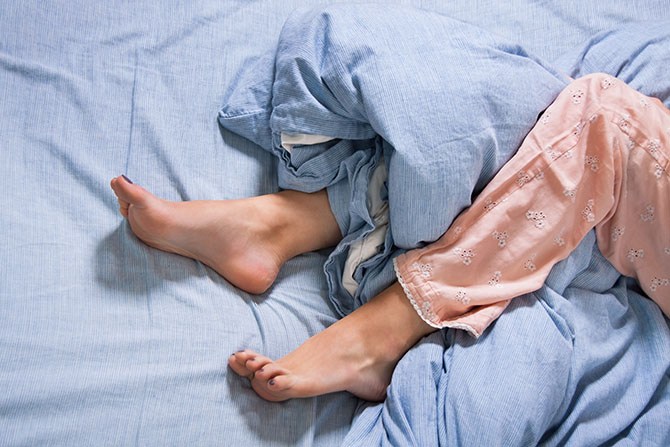
Restless leg syndrome (RLS), or Willis-Ekbom Disease, is the strange sensation of twitching, crawling or jerking of the legs as well as a strong urge to move them. Symptoms are most prevalent at night and while lying down but may occur during long periods of sitting. Moving the legs brings only momentary relief, so the continuous urges to move become annoying and contribute to restless sleep. While RLS may begin at any age, middle-aged and older people tend to have more severe symptoms. The syndrome affects both men and women, however women are likely to suffer more. RLS may be either primary, which has no known cause, or secondary, which is caused by other conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary in duration, severity, and occurrence from person to person.
- Fatigue as a result of not getting enough sleep
- Feeling need to get up or walk after sitting or sleeping for only a short time
- Strong desire to move the legs
- Uncomfortable sensations in the legs (itching, numbness, feeling ticklish, burning sensation)
Causes
Both the muscles and the arteries spasm in restless leg syndrome. Primary RLS appears to have a hereditary component as it often runs in families and it typically begins at an early age. Although the cause of Primary RLS is unclear, research continues on a potential relationship between RLS and dopamine neurotransmitter dysfunction and brain iron deficiency.
Secondary RLS is known to be induced by the following:
- Anxiety
- Caffeine
- Certain medications
- Food allergies
- Malabsorption of nutrients
- Nutritional deficiencies of magnesium, folic acid or iron
- Smoking
- Stress
This condition is common during pregnancy which suggests hormones may also play a role. Magnesium is lost when consuming caffeinated beverages and during periods of stress. RLS can also be a symptom of conditions such as MS, kidney failure, diabetes, and neuropathy.
Prescription for Health
Diet
If RLS is due to low iron, add high iron foods to the diet. If low folate and magnesium are indicated, increase foods high in these nutrients. Some examples are:
- Beet greens
- Organic liver
- Pumpkin seeds
- Shellfish
- Spinach
- Swiss chard
Avoid eating foods high in iron near foods high in calcium as calcium hinders iron absorption. Avoid caffeine and alcohol near magnesium and folate containing foods as these will inhibit nutrient absorption.
| Nutrient | Dosage | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium glycinate or threonate | 500 mg after every meal. If you have kidney problems consult your physician before taking this dosage of magnesium. | Alleviates symptoms of restless leg syndrome, heart palpitation, and twitching eyelids. If you are a heavy coffee drinker, you need more magnesium (100 mg for every cup of coffee consumed). |
| BioFe® Iron (Micronized, microencapsulated iron pyrophosphate III) | 15 mg twice daily | Reduces restless legs when serum ferritin levels are restored |
| Coenzyme fully reacted B-complex | Look for a minimum of the following per daily dose: B1 – 100mg B2 – 7.5 mg Niacin – 353 mg B5 – 300 mg B6 – 100 mg B12 – 1000 mcg Folate – 1000 mcg | Prevents deficiency, is important for nerve and muscle function |
| Vitamin E | 100 IU three times daily | Alleviates symptoms promptly |
| Valerian or kava kava | Tincture as directed | Calms and relaxes nerves |
| Ginkgo biloba, standardized extract | 60 mg twice daily | Research has shown ginkgo improves circulation in the legs |
Health Tips to Enhance Healing
- Avoid caffeinated beverages (coffee, tea, cola, cocoa). Food supplements and pain medications may also contain caffeine; read labels.
- Drink herbal teas, especially chamomile.
- Eat magnesium-rich foods.
- Reduce stress.
- Take supplements away from alcohol and caffeine to ensure absorption.